Choice Privileges A Critical Examination
Choice privileges, the often-unacknowledged advantages afforded to certain individuals based on various factors, are a multifaceted concept demanding careful consideration. This examination delves into the nuanced definition of choice privileges, exploring their historical context and societal implications. We’ll analyze how these privileges manifest in different aspects of life, from personal choices to professional opportunities, and how they impact various groups within society.
The discussion will explore the complex interplay of factors influencing the distribution of choice privileges, including socioeconomic status, cultural norms, and personal characteristics. We’ll also delve into the potential positive and negative consequences of these privileges, highlighting potential disparities and inequalities. Ultimately, we’ll propose strategies for fostering equitable choice privileges, promoting access for all, and achieving a more just society.
Defining Choice Privileges
Choice privileges refer to the advantages and opportunities afforded to individuals based on their inherent characteristics, societal positions, or access to resources. These privileges often grant them greater freedom and autonomy in making choices, impacting various aspects of their lives, from personal decisions to professional advancements and social interactions. This concept acknowledges that not everyone enjoys the same level of freedom and access, highlighting the disparities in opportunities and power structures.
A deeper understanding of choice privileges reveals how they shape individual trajectories and contribute to existing societal inequalities. This understanding is crucial for fostering a more equitable and just environment where everyone has the potential to exercise their choices freely and effectively.
Core Concepts of Choice Privileges
Choice privileges are not simply the ability to make choices; they are the inherent advantages and opportunities that influence the outcomes of those choices. These advantages are often embedded within social structures and systems, providing individuals with greater access to resources, information, and support. This often translates into more effective decision-making and more favorable outcomes.
Historical and Societal Contexts
The concept of choice privileges has evolved alongside societal structures. Historical power imbalances, such as those based on gender, race, socioeconomic status, and other factors, have created and maintained disparities in access to resources and opportunities. This historical context continues to shape present-day societal structures and influence the range of choices available to individuals. For instance, women historically faced significant limitations in their professional and educational choices, demonstrating how historical contexts profoundly affect present-day opportunities.
Examples of Choice Privileges Across Domains
Choice privileges manifest in various domains, impacting personal, professional, and social spheres. These privileges can be subtle yet powerful, influencing the range of options available to individuals.
- Personal Choice: Having the financial resources to pursue higher education, travel extensively, or choose a lifestyle aligned with personal values. This freedom to choose a desired lifestyle is often unavailable to those facing financial constraints. For example, someone with significant financial resources can easily afford a personalized educational program or specialized training tailored to their interests.
- Professional Choice: Having access to high-quality education and networking opportunities, leading to better job prospects and career advancement. This privilege allows for greater professional mobility and career growth. For example, someone with a well-connected network can find job opportunities faster and with better compensation than someone without such connections.
- Social Choice: Being able to navigate social situations without facing discrimination or prejudice. This privilege grants individuals the ability to engage in social interactions without the fear of marginalization or exclusion. For instance, a person belonging to a dominant social group can participate in social events without experiencing barriers or biases, allowing them to form connections and engage in activities with ease.
Types of Choice Privileges and Their Implications
This table contrasts different types of choice privileges with their respective implications.
| Privilege Type | Description | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Choice | Freedom to make decisions regarding personal life, including lifestyle choices, education, and healthcare. | Influences personal well-being and opportunities for self-fulfillment. | Access to quality healthcare and specialized medical treatment based on financial capacity. |
| Professional Choice | Opportunities for career advancement, including access to resources, mentorship, and networking. | Impacts career progression and earning potential. | Networking opportunities in professional fields, enabling faster career advancement. |
| Social Choice | Freedom to interact with others without facing discrimination or prejudice. | Shapes social experiences and participation in community life. | Navigating social situations without experiencing bias or discrimination based on race, gender, or other factors. |
Impact of Choice Privileges

Choice privileges, the ability to make autonomous decisions regarding various aspects of life, are a cornerstone of many societies. Understanding their impact is crucial, as it reveals both potential benefits and drawbacks, and how they affect different groups. This examination will delve into the positive and negative consequences of choice privileges, their effects on diverse populations, and the resulting inequalities.
Positive Consequences of Choice Privileges
Choice privileges empower individuals by granting them agency over their lives. This agency can lead to increased self-esteem and personal growth as individuals take ownership of their choices and their outcomes. Furthermore, the freedom to make decisions can foster innovation and creativity, leading to progress in various fields. The ability to choose one’s career path, for example, can result in individuals pursuing their passions and contributing to society in ways they deem meaningful.
Negative Impacts of Choice Privileges
While choice privileges offer opportunities, they also carry potential downsides. An overemphasis on individual choice can lead to a sense of isolation or detachment from others. It can also result in individuals feeling overwhelmed by the multitude of choices available, potentially hindering their decision-making processes. Additionally, the pressure to make the “right” choice can induce stress and anxiety. Moreover, choices made in the absence of adequate information or support can have unintended negative consequences.
Impact on Different Groups
Choice privileges are not equally distributed across all groups. Socioeconomic status, cultural background, and access to resources significantly influence the extent to which individuals can exercise choice. For instance, individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds may face barriers to accessing information or resources necessary to make informed choices, leading to disparities in opportunities. These disparities can perpetuate existing inequalities and create further marginalization. Similarly, individuals with disabilities or limited mobility may face challenges in exercising their choices related to housing, transportation, or employment.
Disparities and Inequalities Related to Choice Privileges
The unequal distribution of choice privileges can result in significant disparities. For example, access to quality education, healthcare, and employment opportunities varies widely based on factors such as socioeconomic status, race, and gender. These disparities can perpetuate cycles of disadvantage, hindering individuals from reaching their full potential. Individuals without access to these resources may face limited choices and opportunities, creating a cycle of disadvantage.
Perspectives on Choice Privileges
| Perspective | Arguments | Potential Biases |
|---|---|---|
| Individual | Choice privileges are essential for personal growth and fulfillment. They allow individuals to pursue their passions and shape their lives according to their values. | Individuals may overemphasize the importance of their own choices, potentially overlooking the impact of external factors or the needs of others. |
| Group | Collective choice-making can empower groups to achieve shared goals and address collective challenges. However, there is a risk that group decision-making may neglect the needs of individual members. | Group biases, such as conformity pressures or the marginalization of dissenting voices, can influence decision-making processes. |
| Societal | Choice privileges contribute to societal progress by fostering innovation, diversity, and economic growth. However, the unequal distribution of these privileges can lead to social unrest and inequality. | Societal perspectives may be influenced by prevailing ideologies, power structures, and historical biases. |
Factors Influencing Choice Privileges

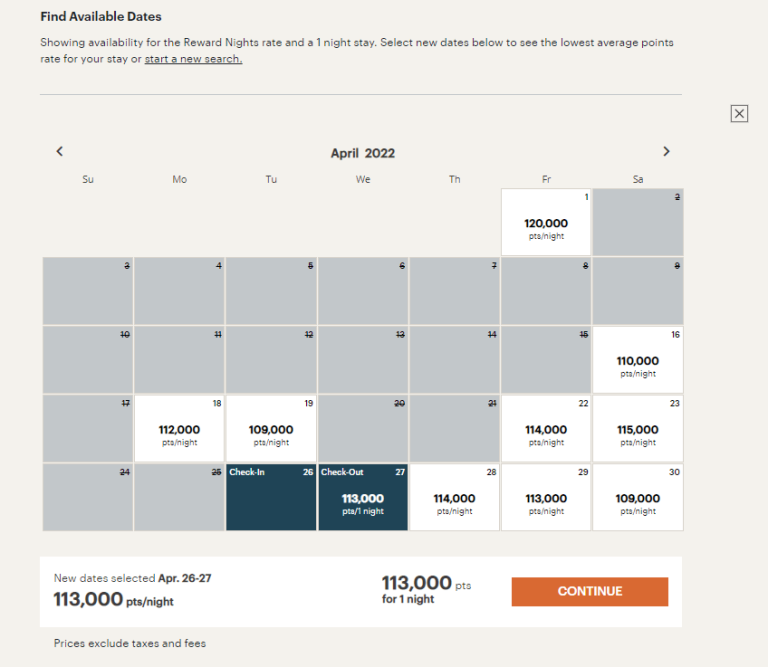
Source: loyaltylobby.com
Choice privileges, the uneven distribution of opportunities and resources based on various factors, are a complex phenomenon. Understanding these factors is crucial to recognizing and addressing the systemic disparities that shape individuals’ and groups’ access to opportunities. These factors are deeply interconnected and often operate in a reinforcing manner, creating cycles of advantage and disadvantage.
A range of influences, from socioeconomic status and cultural norms to personal characteristics, all contribute to the shaping of choice privileges. Examining these factors reveals the intricate interplay of individual agency and societal structures in determining access to resources and opportunities. Recognizing these influencing factors is the first step towards creating a more equitable and just society.
Socioeconomic Status
Socioeconomic status (SES) significantly impacts access to choice privileges. Individuals from higher socioeconomic backgrounds often have greater access to resources, education, and networks that enhance their opportunities. This includes better access to quality education, healthcare, and financial resources. These advantages can create a self-perpetuating cycle where those with higher SES have greater opportunities, further solidifying their position of privilege. For example, children from affluent families may have access to tutors and extracurricular activities that enhance their skills and knowledge, giving them a head start in life. Conversely, those with lower SES may face barriers like inadequate housing, limited access to nutritious food, and fewer educational opportunities.
Cultural Norms
Cultural norms play a significant role in shaping choice privileges. Societal expectations, traditions, and beliefs often determine the opportunities available to different groups. For instance, certain cultures may value specific skills or professions, creating barriers for those who do not align with these norms. Cultural norms also affect access to resources and opportunities within specific communities, leading to disparities in the distribution of choice privileges. Furthermore, cultural expectations can impact personal characteristics and choices, contributing to the development of these privileges. For example, a culture that emphasizes traditional gender roles might limit opportunities for women in certain fields.
Personal Characteristics
Personal characteristics, including skills, knowledge, and personality traits, also influence choice privileges. Individuals with strong communication skills, leadership qualities, or specific knowledge in high-demand fields are often better positioned to seize opportunities. Moreover, personal resilience, adaptability, and the ability to navigate social situations effectively can significantly impact access to resources and opportunities. However, personal characteristics are often influenced by the socioeconomic and cultural contexts in which they develop. For instance, someone with exceptional leadership qualities might struggle to access opportunities if they lack the necessary resources or networks.
Factors Influencing Choice Privileges: Summary Table
| Factor | Description | Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic Status | Refers to an individual’s or family’s position in society based on factors like income, education, and occupation. | Higher SES often correlates with greater access to resources, opportunities, and networks. | Children from affluent families may attend private schools with advanced facilities and resources. |
| Cultural Norms | Societal expectations, traditions, and beliefs shape behavior and opportunities. | Cultural norms can create barriers or advantages depending on individual alignment with these norms. | Certain cultures may favor specific professions, limiting opportunities for individuals outside those fields. |
| Personal Characteristics | Individual skills, knowledge, personality traits, and resilience. | Strong personal characteristics can enhance opportunities but are often shaped by socioeconomic and cultural contexts. | Individuals with strong communication skills might have greater success in negotiations and securing opportunities. |
Strategies for Equitable Choice Privileges
Choice privileges, when implemented fairly, empower individuals and foster autonomy. However, existing inequalities can create barriers to accessing these privileges, leading to disparities in opportunities and outcomes. This section explores strategies to mitigate these disparities and promote equitable access to choice privileges for all.
Addressing disparities in choice privileges requires a multi-faceted approach. By combining policy changes, educational initiatives, and community engagement, we can create systems that are more inclusive and responsive to the needs of diverse populations. This section articulates specific methods for achieving equitable choice privileges, highlighting successful programs and the challenges involved.
Policy Change
Policies are foundational in establishing fair access to choice privileges. These policies must be clearly articulated, transparent, and consistently enforced. They should explicitly address potential biases and promote equal opportunities. A key aspect of policy change is the inclusion of specific criteria for evaluating and addressing any disparities identified within the existing system.
- Eliminating discriminatory language and practices: Policies should explicitly prohibit any language or practices that discriminate against certain groups. This includes reviewing existing policies for discriminatory language or implicit bias and replacing them with inclusive language and practices. For example, a policy that states “priority is given to those who have demonstrated consistent good performance” could be revised to explicitly state the criteria for evaluating performance to avoid implicit bias towards particular demographic groups.
- Establishing clear criteria for selection: Policies should establish transparent and objective criteria for evaluating applicants. The criteria should be measurable, relevant to the privilege in question, and applied consistently across all applicants. This will ensure that selection processes are not influenced by subjective factors that can lead to inequities.
- Implementing mechanisms for regular review and revision: Policies must be subject to periodic review and revision to ensure they remain relevant and equitable in the face of changing circumstances. This includes feedback mechanisms to address issues or concerns from the community or relevant stakeholders.
Educational Initiatives
Providing education and awareness can empower individuals to effectively exercise their choice privileges. By promoting understanding of the importance of choice and its impact, individuals can be better equipped to make informed decisions.
- Training programs for administrators and staff: Training programs can equip those responsible for administering choice privileges with the knowledge and skills needed to implement them equitably. This includes training on identifying and addressing potential biases and ensuring consistency in application procedures. A successful example includes programs that train teachers on culturally responsive teaching practices to help them better understand and meet the needs of diverse students.
- Public awareness campaigns: Raising awareness about the importance of equitable choice privileges can promote understanding and support for policy changes and programs designed to address disparities. These campaigns should target diverse communities and utilize various communication channels to reach a wide audience. Examples include targeted public service announcements, community workshops, and online resources.
- Educational materials for beneficiaries: Providing clear and accessible information about choice privileges, their benefits, and how to navigate the system can empower individuals to exercise their rights effectively. This includes creating clear and accessible resources, in multiple languages if necessary, for individuals who may not be familiar with the procedures or have limited access to information.
Community Engagement
Active engagement with diverse communities is essential to understanding their needs and preferences regarding choice privileges. This involves gathering feedback, addressing concerns, and tailoring programs to best meet their specific requirements.
- Community forums and consultations: Hosting regular forums and consultations can provide a platform for community members to voice their concerns, share ideas, and offer feedback on policies and programs related to choice privileges. These platforms can also provide opportunities for community members to share their experiences and perspectives on what works and what does not work. This is vital for creating equitable access to resources.
- Partnership with community organizations: Collaborating with community organizations that serve specific populations can ensure that programs reach the most vulnerable and marginalized groups. These partnerships can help to tailor programs to specific community needs and preferences, and to increase participation from underrepresented groups.
- Monitoring and evaluation: Regularly evaluating the impact of programs and policies is critical to identifying areas for improvement and ensuring that choice privileges remain equitable. This includes gathering data on program participation, satisfaction levels, and outcomes to assess their effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
| Strategy | Description | Potential Benefits | Challenges ||—|—|—|—|| Policy Change | Revising existing policies to ensure fairness and inclusivity | Improved equity, transparency, and accountability | Requires political will and overcoming resistance to change || Educational Initiatives | Training programs for staff and beneficiaries, public awareness campaigns | Increased understanding and engagement, improved implementation | May require significant resources and sustained effort || Community Engagement | Community forums, consultations, and partnerships | Improved program design and delivery, greater community support | Requires significant time commitment and collaboration |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, choice privileges are a powerful force shaping individual and societal outcomes. Understanding their multifaceted nature, impacts, and underlying factors is crucial for creating a more equitable and just society. The discussion underscores the importance of recognizing and addressing the inequalities embedded within these privileges, paving the way for strategies that promote equal opportunities and empower all individuals to make informed choices.